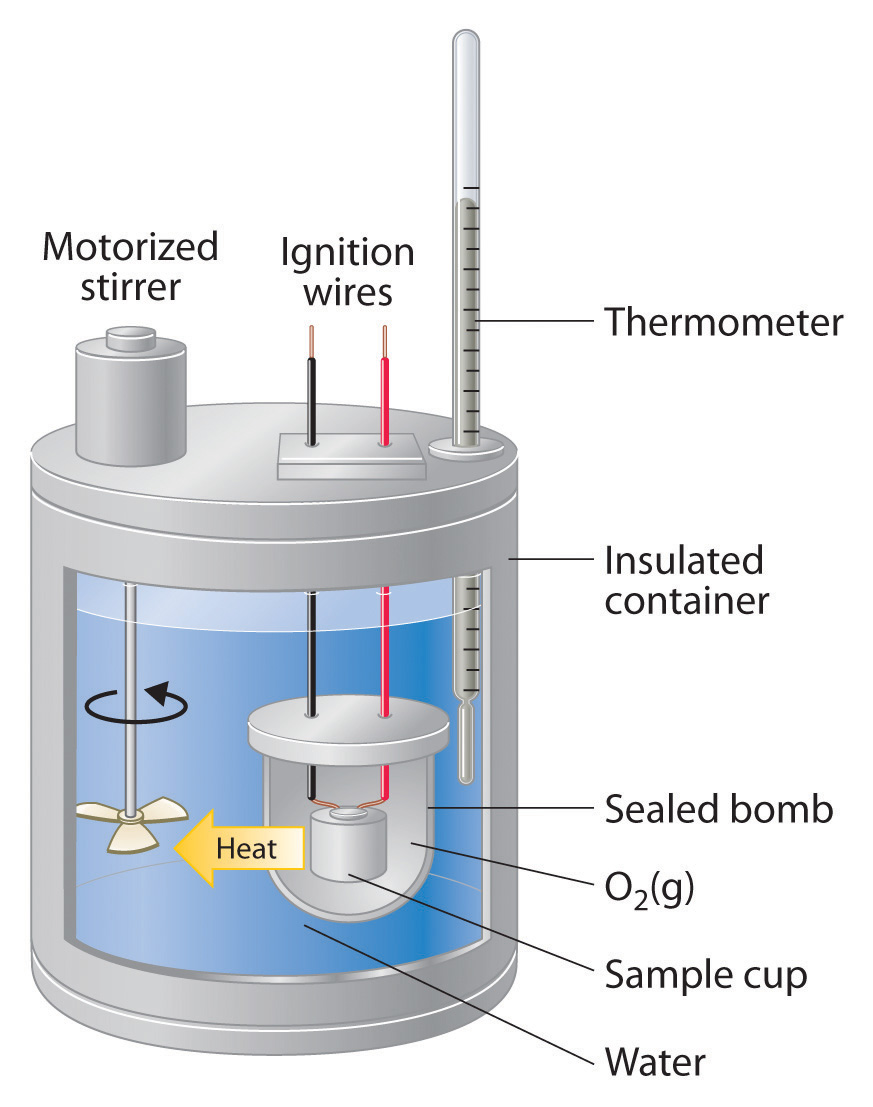
Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary . Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in. Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. Lab session 9, experiment 8: The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or.
from sites.google.com
Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Lab session 9, experiment 8: Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes.
Calorimetry Preliminary HSC Chemistry
Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Lab session 9, experiment 8: One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt).
From www.docsity.com
Calorimetry lab report Study Guides, Projects, Research Chemistry Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Lab session 9, experiment 8: Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. One. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From deborahsilvermusic.com
Calorimetry Lab Specific Heat Capacity, 59 OFF Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From sites.google.com
Calorimetry Preliminary HSC Chemistry Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Lab session 9, experiment 8: Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Q =. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Experiment 25 Report Sheet Calorimetry Lab Sec Name Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Lab session 9, experiment 8: Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Equation For Constant Volume Calorimetry Tessshebaylo Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s),. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Use the References to access important values if Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From users.highland.edu
Calorimetry Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Lab session 9, experiment 8: One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. Q = mcδt, where. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From answerhappy.com
CALORIMETRY HEAT CAPACITY OF A CALORIMETER NTRODUCTION Lab Data Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.bartleby.com
Answered Experiment 14 Data and Calculations… bartleby Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.thinkswap.com
Calorimetry Lab Report PHYS1006 Foundations of Physics Curtin Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED In the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, Or constant Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From cityraven.com
👍 Heat effects and calorimetry lab answers. Heat Effects And Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. Ntity of. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From garyspierceo.blob.core.windows.net
Bomb Calorimeter Equation With Water at garyspierceo blog Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in. One technique we can use to measure the amount of heat involved in. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From webapi.bu.edu
⚡ The cold equations analysis. The Cold Equation By Tom Godwin Analysis Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.pinterest.com
Calorimetry Lab Report in 2022 Science diagrams, Lab report Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Lab session 9, experiment 8: Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in. The specific heats of gases depend on what is maintained constant during the heating—typically either the volume or the pressure. Purpose explore how the specific heat of a. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From porter-yersblogvega.blogspot.com
Heat Capacity of Calorimeter Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Ntity of heat exchanged in chemical and physical processes. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Purpose explore how the specific. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.studocu.com
Copy of Lab 5 Calorimetry and Specific Heat Lab Calorimetry and Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Lab session 9, experiment 8: Specific heat is an intensive property of a single phase (solid, liquid or gas) sample that describes how the temperature. Purpose explore how the specific heat of a substance can be determined. The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.
From www.youtube.com
Calorimetry Calculate Specific Heat YouTube Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary Lab session 9, experiment 8: The amount of heat absorbed or released (q) by the object depends on its mass (m), specific heat (c s), and the change in temperature (δt). Heat is a form of energy associated with the motion of atoms or. Q = mcδt, where q is the symbol for heat transfer (“quantity of heat”), m is. Lab Calorimetry And Specific Heat Summary.